Caffeine is a natural and bitter-tasting substance that acts as a stimulant. Although too much caffeine may have undesirable outcomes, drinking coffee in moderation may lower risk of developing certain cancers and diabetes.
Sources of Caffeine
Caffeine is naturally found in coffee beans, certain tea leaves (e.g. black tea, green tea) and cocoa beans. Caffeine is a food additive and is added to energy drinks, colas and other soda pops.
Effects of Caffeine on Your Body
By stimulating the central nervous system, caffeine helps increase alertness, reduce fatigue and improve concentration. Once in the stomach, caffeine stimulates the release of acid, which causes some to experience heartburn and indigestion.
Different people show different levels of sensitivity to caffeine. Those who are more sensitive may experience difficulty falling sleep, irritability and nervousness, increased heart rate and even headaches.
In all users, excessive caffeine may result in unpleasant symptoms such as headache, dizziness, nervousness, insomnia, racing heart or abnormal heartbeat and increased blood pressure.
Caffeine Should be Consumed in Moderation
Adults 19 years of age and over should not exceed 400 milligrams of caffeine per day. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should limit this to 300 milligrams per day. Children and adolescents should not have more that 2.5 milligrams of caffeine per kilogram of their body weight.
Level of Caffeine in Common Drinks
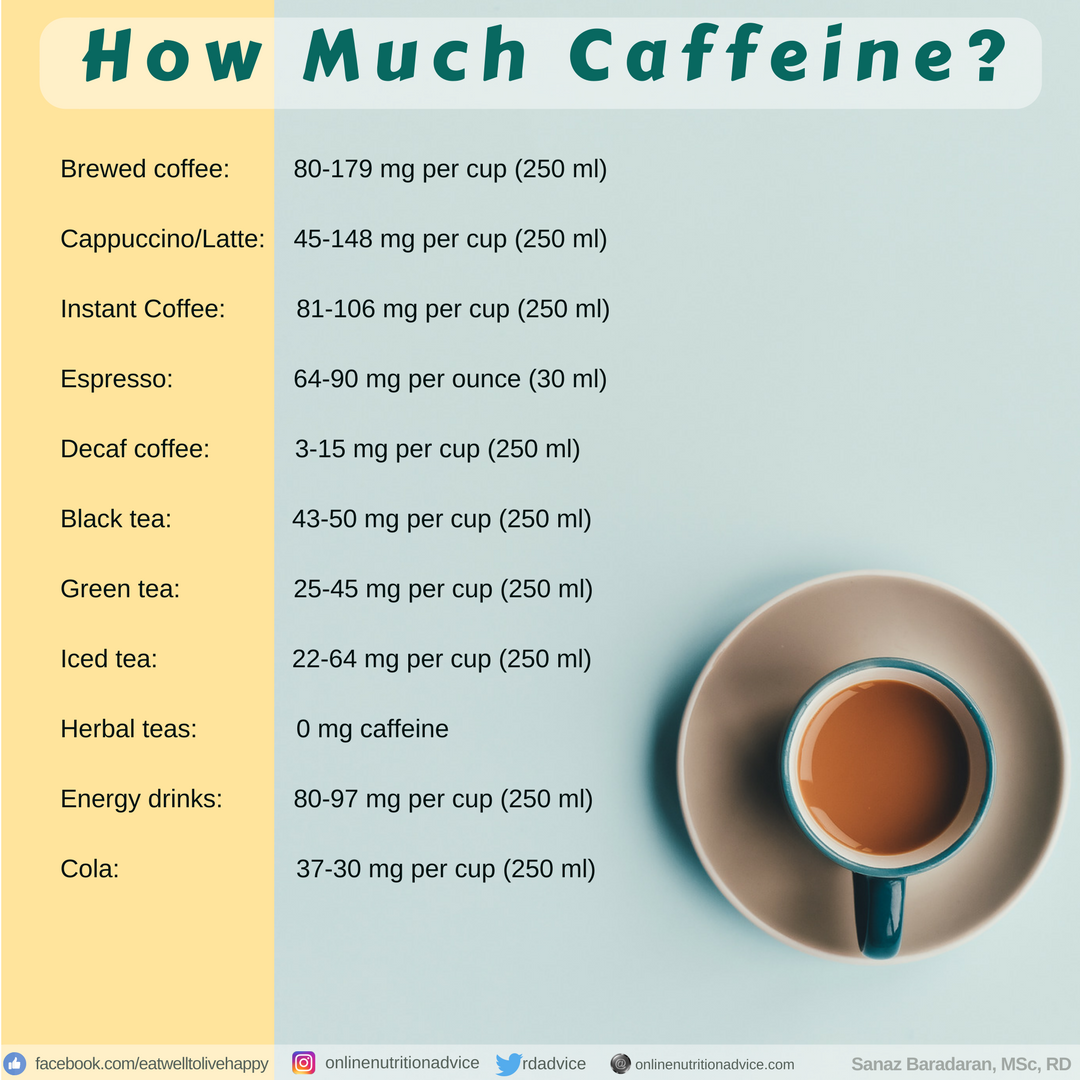
So Should I be Avoiding Coffee?
Consuming everything in moderation is key! Research shows that caffeine may even impose health benefits if eaten within recommended amounts.
References:
Cleveland Clinic. (2014, July 13). Caffeine: What is it, how is it used, tips for breaking the habit. Retrieved from http://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/caffeine-tips-for-breaking-habit
Eat Right Ontario. (2016, October 9). Eat Right Ontario – Facts on Caffeine. Retrieved from https://www.eatrightontario.ca/en/Articles/Caffeine/Facts-on-Caffeine.aspx
International Food Information Council Foundation: “Caffeine & Health: Clarifying the Controversies.” 2008. www.ific.org Accessed 6/2014.
Wang, A., Wang, S., Zhu, C., Huang, H., Wu, L., Wan, X., … & Sang, X. (2016). Coffee and cancer risk: A meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Scientific Reports, 6.
